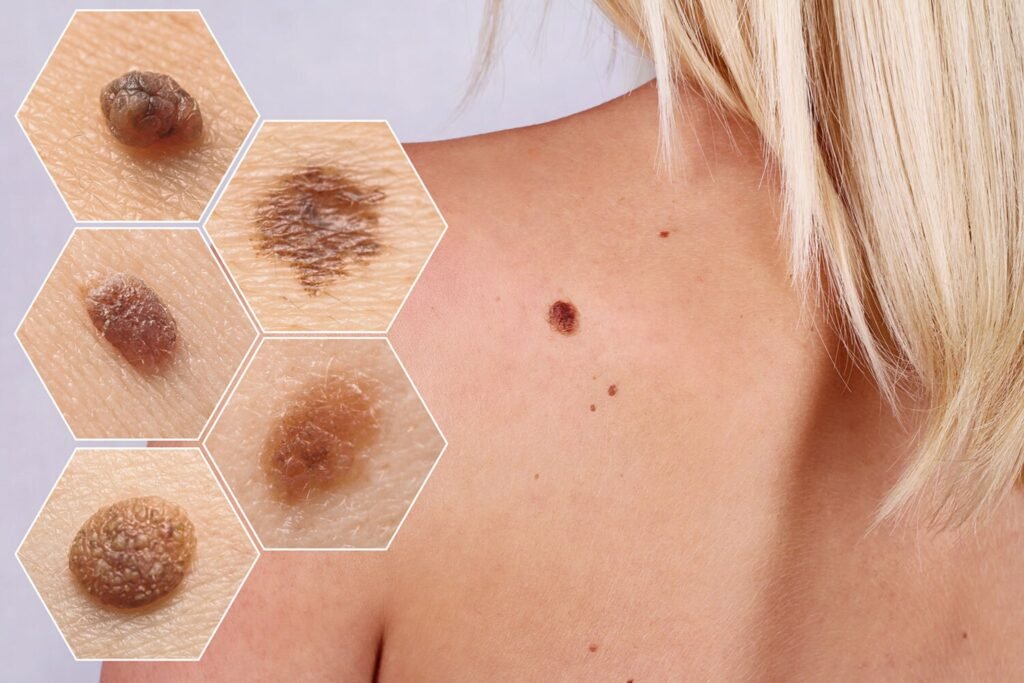
What is a skin tumor?
All lesions that are present in any part of the body, either congenitally or later, in skin color or different colors, at the same level as the skin or raised from the skin or located under the skin are called skin tumors. Skin tumors, commonly known as “moles”, are the most common. Moles are generally benign, but they can also be associated with skin cancer.
NEVUS (MOLE)
Masses commonly known as “moles” are millimetric masses that can appear anywhere on the body or are present congenitally, raised from the skin or in the skin, the same color as the skin or different color.
Moles can be named according to the skin layer they are located in, their color or the cells they contain; such as epidermal nevus, melanocytic nevus, blue nevus, ota nevus. Moles are generally benign formations. They can rarely turn bad in older ages. In general, it is recommended to remove moles that show signs of worsening such as an increase in size, change in color, irregularity in the borders, bleeding and ulceration.
If the problem-free moles visually disturb the patient, or if they are in a place that is constantly exposed to trauma such as the beard area, belt, bra area, or scalp, it is recommended to remove them.
Moles can be cauterized, frozen, lasered, or surgically removed. The method to be used is decided according to the mole’s characteristics, location, and size. Surgical removal is a short procedure. After the mole is removed, tissue integrity is ensured with appropriate stitches and an appropriate repair is performed with the aim of leaving an invisible scar behind. After the mole is removed, the person can immediately return to work and social life. Recovery is short-lived in these procedures, which are applied on an outpatient basis.
BASAL CELL CANCER
It is a skin tumor that originates from the cells at the base of the skin and has a slow spreading and growth potential. It generally occurs over the age of 40, and is more common in women and those with fair skin. It occurs especially in the face area exposed to the sun and most frequently in the nose. It can be like a raised crusty wound on the skin and can appear as an ulcerated bleeding mass. It slowly grows over the years and begins to affect the surrounding tissues. It can be completely treated with surgical removal. The approximately 1 cm healthy area around the tumor is also removed during surgery to prevent recurrence. Tumors removed in the face area can be repaired with tissue flaps prepared from the surrounding tissues or with grafts called skin patches. Although it is classified as cancer, basal cell cancer progresses as a relatively benign formation.
SLAUGHTER CELL CANCER
It is a type of skin cancer that occurs especially in the face area around the lips. Smoking triggers its emergence. Squamous cell cancer grows slowly but has the potential to spread to surrounding tissues. It can spread to the lymph nodes in the neck, lungs, and brain. Non-healing wounds around the lip and surrounding areas may be precursors to squamous cell cancer. Therefore, a biopsy must be taken from a lesion that occurs in this way, and if squamous cell cancer findings are detected, treatment must be started immediately. Surgical removal of the tumor and repair of the resulting tissue loss with surrounding tissues are necessary. If there is spread to the neck lymph nodes, neck dissection may be required or radiotherapy may be applied to the neck.
MALIGNANT MELANOMA
The most feared type among skin tumors is malignant melanoma. It is generally a tumor that spreads rapidly to internal organs and poses a life-threatening threat. It is rare but very aggressive. It usually appears as dark-colored moles in middle-aged individuals. It is often seen in the face area, but it can occur anywhere on the body, especially on the nails, soles, and nervous system mucosa. In its treatment, the tumor must be removed along with a large, sufficient amount of healthy tissue around it and the resulting tissue loss must be repaired with plastic surgery methods. Lymph nodes are checked with special methods and, if necessary, they are also removed during surgery. Additional treatments may be required later, depending on organ involvement and lymph node spread. Although malignant melanoma is classified in different ways, the most important criterion in life expectancy is the depth of the tumor.